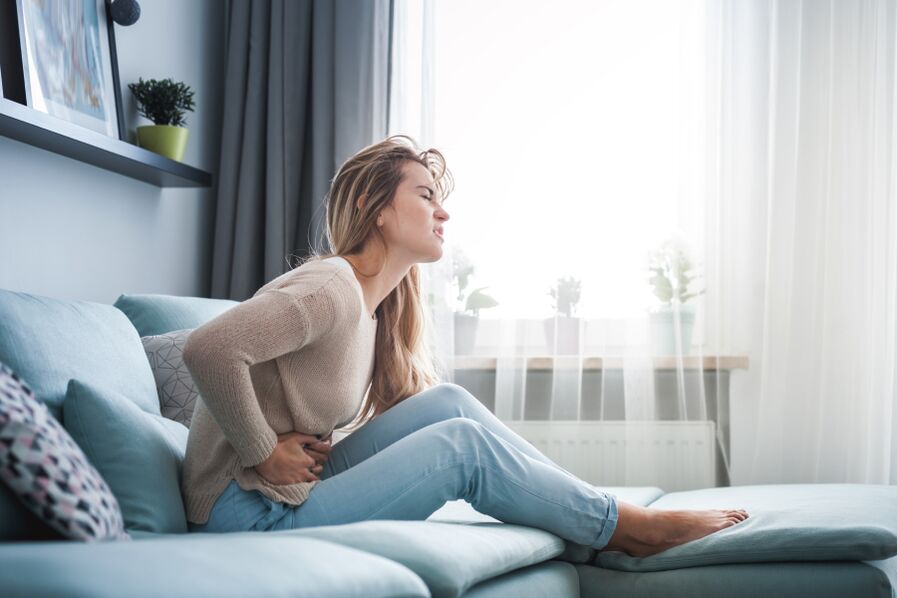
The corresponding, effective and timely therapy of any IMIs leads to a significantly higher frequency of symptomatic and bacteriological cure and better reinfection prevention. Unfortunately, treatment can lead to antibiotic resistance to pathogens and bacteria of comments and have adverse effects on intestinal and vaginal flora, so it is very important to immediately consult a doctor and choose it correctly.
Clinical recommendations for the treatment of acute cystitis without complications
The American Society of Specialists in Infectious Diseases (IDSA) in cooperation with the European Society of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) published clinical recommendations for treatment with cystitis and acute non -complicated pyelonephritis in 2011. This document became an invaluable reference in the IMP. This manual analyzes important factors to choose the optimal treatment:
- the nature of the resistance of the uroopathogens;
- Sensitivity of upatogenic bacteria to antimicrobial medications;
- The possibility of side effects of antimicrobial medications.
As for sensitivity, two important facts are observed in this leadership:
- The stability of uroopathogens to antibiotics has increased in recent years;
- The nature of resistance demonstrates a significant geographical variability between countries and even regions.
Therefore, recommendations review periodically due to the constant development of resistance, the development of new tools and the conduct of research that show the superiority and inefficiency of medicines. According to recommendations and research, the requirements for medications for the treatment of uncomplicated cystitis, the following substances are better met: the following substances:
- phosphomycin;
- nitrofurantin.
The following selection criteria were used: pharmacokinetics, interaction, the probability of hitting (the probability that the microorganism is sensitive to antibiotics), the development of resistance, the specific use for the IMP, the effectiveness, the side effects, the dose frequency, the duration of the treatment, the cost.
The study included the following drugs: amoxicillin (with or without clavulanic acid), nitrofurantine, sulfametizol, trimtoprime, co-trrhyxazole, ciprofloxacin, norphloxacin, offloxacin and trometamol of phosphomicine.
Characterization of the first line of infections of the lower urinary tract
Table 1. First line for the treatment of cystitis
Trometamol phosphomycin
Phosphomycin was opened in 1969 as representative of the new phosphon antibiotic class.
Active substance: phosphomycin. Liberation form: granules for the preparation of the solution, in packaging 1 or 2 packages, dose of phosphomicin 3 g/bag, 2 g/bag.
It refers to the clinical and cultural group to roantiseptics, antibiotics (phosphonic acid derivatives).
Action spectrum
Phosphomycin has a bactericidal activity of a broad spectrum of action in relation to:
- Staphylococci (Staphylococcus spp. );
- Enterococci (Enterococcus spp. );
- Haemophilus spp;
- The majority of intestinal gram-negative bacteria, including 95. 5% E. coli, producing β-lactamases of the expanded spectrum (blrs);
- E. coli strains produced by metal-β-lactamase sensitive to phosphomycin;
- Citrobacter spp. ;
- Enterobacter spp. ;
- Klebsiella spp. , Klebsiella pneumoniae;
- Morganella Morganii;
- Proteus mirabilis;
- Pseudomonas spp. ;
- Serratia spp.
The peculiarity of the drug
- Trometamol phosphomycin is prescribed exclusively for the treatment of uncomplicated acute cystitis in the form of a unique 3 Gy dose not prescribed for pyelonephritis.
- It is better absorbed if you take it before eating.
- It reaches a high concentration in urine and retains a high level for more than 24 hours.
In several studies, the clinical and microbiological effectiveness of phosphomycin was compared with other antimicrobials of the front row with uncomplicated cystitis. The clinical efficiency of a dose (3 g) of phosphomycin is 91% (the cure occurs in 91% of patients). The indicator is comparable to nitrofurantoin (93%), trimetromo-sulfamethoxazole (93%) and fluoroquinolones (90%) in uncomplicated acute cystitis.
Advantages of phosphomicin treatment
The microbiological level of healing phosphomycin (80%) is lower than that of comparable antibiotics in 88-94%. However, a recent meta -analysis of 27 studies did not reveal the differences in the effectiveness between phosphomycin and other antibiotics for the treatment of cystitis and discovered the following facts:
- Phosphomycin causes significantly less adverse reactions, which is the most important, even in pregnant women.
- An additional benefit is to treat resistant multiple microorganisms. Several in vitro studies showed that phosphomicin is active in relation to the Staphylococcus aureus resistant to vanic and the gram -negative sticks that produce blr.
- Effective in the treatment of IM caused by K. Pneumoniae.
- It has a minimum side effect on the body. This is indicated by the high frequency of the susceptibility of E. coli in regions with frequent use of phosphomycin with uncomplicated cystitis in women;
- Convenience of a single dose mode.
Indication
- acute cystitis (bacterial origin);
- Exacerbation of recurrent cystitis (bacterial origin);
- urethritis (non -specific bacterial);
- Bacteriuria of asymptomatic pregnant women;
- Imp after operations;
- Prevention of imp.
Dose and application method
Children (5 years) - 2. 0 g once
Second trick: 3. 0 g 24 hours after primary school
Recommendations for use
- Follow all the instructions on the label.
- Phosphomycin is generally prescribed only in one dose.
- Do not take large/smaller amounts or more if it is not prescribed by a doctor.
- It can be used simultaneously/after eating.
- Phosphomycin is a drug powder, before using it, it must be diluted with water. Do not take dry dust without adding water.
- Dissolve a 1/2 cup of cold water, mix and drink immediately. You can add a little more water to the same glass, stir carefully and drink immediately to guarantee a complete dose.
- Do not mix with hot water.
- It is good to take it during the night. There will be a longer break between urine, which will guarantee a longer presence of the medicine in the bladder and a more effective effect.
- Store at room temperature away from moisture and heat in the original packaging.
Other instructions:
- The symptoms cannot go completely immediately, after 2-3 days;
- It is necessary to contact a urologist if the symptoms do not disappear within 3 days after treatment, fever or other complaints will appear;
- Before applying to the patient, it is recommended to consult a doctor to make sure phosphomicin is an adequate antibiotic for treatment. In addition, urine analysis may be required before and after taking this medication.
Contraindications:
- Children under 5 years;
- allergic reactions to the components;
- Severe renal failure.
General side effects:
- nausea, stomach disorder, light diarrhea;
- Headache, dizziness;
- Itching or vaginal secretion (rarely).
Drug interaction
Simultaneous intake with Meteteclopramida is not recommended to avoid weakening the action of phosphomycin.
Therefore, the convenience of a single dose regime, in vitro activity in relation to resistant gram sticks that cause simple and immature cystitis without complications, And the minimum lateral damage makes phosphomicin a useful option in the treatment of lower MVP infections (cystitis, urethritis).
Nitrofurantin
Active substance: nitrofurantin. Liberation form: tablets, dose 100 mg, 50 mg.
It refers according to the clinical and culture group for roantiseptic, antimicrobials.
Nitrofurantin, related to the group of synthetic Nitrofurans, originally presented in a microcrystalline form. In 1967, Macrocrystalline form with improved gastrointestinal tolerance was available.
Currently, there are two main types of nitrofurantine: a macrocrystalline form and a mixture of microcrystalline and macrocrystalline forms (25 mg of macrocrystals plus 75 mg of monohydrate). Mixed species in the double -birth patented system, in the Russian Federation, are not registered and are not in circulation.
THE MECHANISM OF ACTION
Nitrofurantin bacterial activity mechanisms include several sites:
- inhibition of ribosomal transmission;
- Damage to bacterial DNA;
- Intervention in the CREB cycle.
Nitrofurantina is active in relation to:
- More than 90% of the intestinal strains that cause the IM;
- Enterococcus, including vancomycin resistance;
- Klebsiella spp. ;
- Proteus spp. ;
- Staphylococci (gold and saprophytic) are generally susceptible.
Drug resistance is rare, probably due to multiple areas of the drug. However, Proteus, Serratia and Pseudomonas have natural resistance to nitrofurantoína.
Nitrofurantino can also be an additional option for oral antimicrobial treatment of uncomplicated acute cystitis caused by BLR bacteria producers.
Pharmacokinetics Absorption improves when eating. Nitrofurantine concentrations in serum are low or not defined at standard doses, the content of the prostate gland is not detected. It is excreted mainly with urine, where drug concentration (50 to 250 mg/ml) easily exceeds 32 mg/ml of MPC.
Nitrofurantin should not be prescribed to patients with pronounced renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance<60 m/min), but studies observed high efficiency of the drug in patients with creatinine clearance of 60-30 ml/min.
Sure for use in pregnant women and children.
Indications: Cystitis (bacterial origin) Treatment and prevention.
Dosage. An urologist prescribes it individually based on the severity of the State, the duration and severity of the symptoms.
The usual dose for adults with cystitis:
- 50 to 100 mg oral 4 times a day for 1 week or for at least 3 days after reaching the sterility of urine. The usual dose for adults for cystitis prevention:
- 50 to 100 mg orally once a day before bedtime. Children's dose for the treatment of cystitis:
- 1 month and more: 5–7 mg/kg/day (up to 400 mg/day) orally in 4 doses. The usual dose of children for the prevention of cystitis:
- 1 month and more: 1 to 2 mg/kg/day (up to 100 mg/day) orally in receptions 1-2.
Most experts agree with the recommendation of a 5 -day course of the medicine for the treatment of acute non -complicated cystitis. The studies showed the frequency of early clinical healing with nitrofurantoin from 79% to 95% and the frequency of the microbiological cure from 79 to 92%. In the aggregate of the study of clinical effectiveness, they indicate the general equivalence between nitrofurantoína, prescribed for 5 or 7 days and trimetromo-sulfamethoxazole (pearls), cyproploxacin and a single dose of trometamol phosphomicin (monural). However, the speed of the microbiological cure has constantly demonstrated a slightly more favorable effect for comparison medications.
Recommendations to patients
- It is necessary to follow all the recipes and instructions of the doctor in the instructions for the medicine.
- Do not use large or longer quantities than recommended.
- It is better to take nitrofurantine with food (bioavailability increases).
- It is recommended to observe the reception throughout the prescribed term. The symptoms can pass before, but the treatment cannot stop while the infection is completely eliminated. Dose can increase the risk of greater development of antibiotic -resistant infections and the risk of relapse.
- Nitrofurantin does not treat viral infections, for example, a cold or flu.
Side effect
General side effects:
- Headache, dizziness;
- gase formation, stomach disorder;
- light diarrhea;
- Itching or vaginal secretion.
Much less often they are:
- aqueous or bloody diarrhea;
- Sudden pain or discomfort in chest, whistling, dry cough;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Fever, chills, body pain, fatigue, inexplicable weight loss;
- numbness, tingling or pain in the hands or legs;
- Liver problems: nausea, pain in the upper stomach, itching, feeling of fatigue, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay stool, jaundice (skin yellowing or eye);
- The syndrome similar to Lupido: pain or articular edema with fever, inflamed glands, muscle pain, chest pain, vomiting, thoughts or unusual behaviors, stained eruptions.
Serious side effects can be more likely in older people, in long -term or weakened diseases.
Contraindications:
- Serious disdain of the kidneys excretory;
- kidney failure;
- Oliguria;
- Glucose failure-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- pregnancy;
- age up to 1 month;
- allergic reactions to the components;
- XN II-III stages;
- cirrhosis;
- chronic hepatitis;
- Acute porfiria;
- lactation.
Application in pregnancy
The drug category in relation to pregnancy: in (according to the FDA - EE. UU. ). It is believed that this medicine will not damage a child not born in the early stages of pregnancy. In the last 2-4 weeks of pregnancy, it is contraindicated.
Nitrofurantin can penetrate breast milk, during breastfeeding is not prescribed.
Special instructions
- The risk of peripheral neuropathy increases in the presence of anemia, diabetes mellitus, severe lon, violation of electrolytic balance, the lack of vitamins of group B.
- Nitrofurantine is not used for the treatment of prostatitis, cortical substance lesions, purulent paranephritis. With pyelonephritis, they are not prescribed due to inefficiency.
- Nitrofurantin can give unusual results with some laboratory glucose (sugar) in the urine.
Drug interaction
- With fluoroquinolons it is incompatible.
- Antacids based on trilicato magnesium, unpleasant acid while taking the antimicrobial activity of nitrofurantine.
- The secretion of the channel that blocks the secretion of the channel is not prescribed, since they increase the toxicity of nitrofurantine (the blood content increases), reduce bactericidal properties (the urine content is reduced).
Nitrofurantin is considered the therapeutic remedy of the first line in acute cystitis without complications due to:
- the effectiveness of a 5 -day course;
- a small risk of side effects and damage to the normal flora of a person;
- Minimum bacteria resistance;
- Effectiveness comparable to other antimicrobial medications.